What is Marketing Strategy? Typical Strategies for Beginners

Choosing the right marketing strategy for your business model and goals is an essential factor affecting the future success of your business. So, what marketing strategies do managers need to understand to make the right and most appropriate decisions? Let’s learn more deeply about CleverAds in this article below!
1. What is a Marketing Strategy?
A marketing strategy is a long-term plan so that a business can achieve its goals by understanding customer needs and creating a sustainable competitive advantage in the market. A direct marketing strategy includes processes from determining who your customers are to deciding what communication channels to use to reach those customers.
With a marketing strategy, businesses can determine their current market position, strategic partners need to maintain relationships, and types of advertising and promotions should be deployed over a long-term period. Therefore, it can be seen that making a strategic marketing plan is essential for the success of any business.
2. Positioning Marketing Strategy
This can be understood, as positioning is the position that determines the image of a brand/business in the target customers’ mind.
Since then, the positioning strategy has been formed based on selecting and building in the target customer’s mind a clear and valuable image of the brand/product compared to competitors.
The two main positioning strategies include:
- Competitive Positioning: Compete directly with existing competitors.
- Fill-in positioning: Build a brand new image in the target market.
The target audience can be a product, service, brand, or business itself. In particular, marketers need to distinguish positioning from differentiation.

When using a positioning strategy, businesses should pay attention to providing basic specific images (easy to remember, easy to understand, clear) and these positioning should be based on outstanding attributes that are different. In addition, the positioning of the business also needs to be unique and in line with the demands of the customer.
The positioning image must be established in comparison to the positioning image of competing product brands and must be presented in reality (as promised, reliable, and consistent).
Common errors in the positioning process can include unclear (faint) positioning images, unreliable positioning images, too narrow positioning images, or inconsistent positioning images.
In addition, businesses or brands can reposition when the target customer file changes (aging, rejuvenating, customer needs and wants change, positioning is unclear and effective or not different from competitive positioning, or positioning image becomes negative in the perception of the target customer.
3. Differentiation Marketing Strategy
The concept of differentiation was mentioned in many specialized scientific documents, some of which can be as follows:
Differentiation means self-personalization in the minds of potential objects (included in the concept of positioning). To be different means to use a personalized mindset to protect (attack / fight back) or to become a guerrilla in the battle you participate in to become the winner (Marketing Warfare).
Differentiation means using personalized thought to build a brand (22 Immutable Laws of Marketing).
Differentiation means establishing a personalized strategy. (The Power of Simplicity).
From the above concepts, this can be seen that differentiation is the heart of positioning.
Differentiation strategy is the strategy of differentiating the product (offering), creating its unique point to occupy a special and valuable place in the customer’s mind.
This strategy requires businesses to answer questions such as: How many differentiators need to be created and expanded? How valuable are those differentiators to the target customer?
Some principles of successful differentiation:
- Surprising but interesting
- Difference creates value
- Feel the outstanding value, especially
- Consistent with customers (reasonable cost)
- Communication is possible
- Reliable
- Hard to imitate
4. Competitive Marketing Strategy
Each enterprise entering the market has a definite competitive position relative to its competitors. The competitive position represents the competitive strength of businesses in the market.
For the marketing strategy of the business to be successful it needs to build based on its position in the market and the strategies of its competitors. Competitive strategy is also understood as strategy according to competitive position.
In competition, each business has a competitive position in the market. Competitive position is the position of an enterprise to its competitors, from the point of view of resources that can be exploited to build a competitive advantage.
Competitive position can also be seen as the relative position of the business in the assessment of customers, concerning competitors.
There are 4 types of competitive positions corresponding to 4 strategies in the market

Strategies for the market leader
Some examples of market leaders include Home Depot, Microsoft, IBM, Google, McDonald’s, Nike, Coca Cola. With the leading position in the market, enterprises can deploy strategies such as market expansion, market share protection, and market share development.
Strategies for companies to challenge the market
Market-challenging enterprises are those in the second, third, and relatively large “next” positions, often not resigned or satisfied with the current position but want to develop.
For example, Lowes HP, Explore, KFC, Adidas, and Pepsi, With the position of challenging the market, other businesses can directly or indirectly attack by detour or attack guerrilla.
Strategies for companies following the market
Enterprises of average size and resource capacity often do not want to take the risk of investing in product innovation or pioneering the market.
Examples: Fivimart FPT, Monava, ChickenF, and Tribeco.
This strategy is often applied in industries with homogeneous products and large capital investments such as iron and steel, fertilizers, etc. i.e. the ability to differentiate is very low in terms of products, images, and services, and customers’ products are very price sensitive.
The key strategic direction for the follower is to find ways to increase the loyalty of existing customers and win a share of new customers with a policy of differentiation from the leader (alternatives, complementary services, human relations).
The three main strategies of the follower: are copy, imitate, and improve.
Strategies for companies nestled in the market
Small-scale, resource-constrained firms that are not able to compete in large market segments, are only interested in small market segments and try to occupy market gaps in which they hope to specialize their operations motion.”
Examples: Seven-Eleven, Logitech, Lantabrand, Maple Leaf, Thuong Dinh, and Green Tea LS.
The nesting strategy is suitable for the following market conditions: stable or weak market growth, relatively familiar products, and services, businesses specializing in only a few activities, businesses The industry has earned a reputation for its quality/price relationship, low cost through the narrow assortment, low spending on research and development, product launch and commercial support.
5. Value chain Marketing Strategy
The selected strategy is based on the enterprise’s understanding of the chain of value-creating activities – the global value chain – the value-creation system.
The essence of a value chain strategy is to find ways to create the greatest benefit value for customers based on choosing the value to provide to customers (from understanding customer needs) and finding solutions most effective value delivery method (comparison of value and cost)
When applying this strategy, businesses need to answer the following questions:
- What value?
- What elements constitute value?
- Self-produced or bought out?
- Raise the value inside
Four (4) marketing strategies along the value chain include:
- Low price strategy
- Differentiation strategy
- In-chain strategy: Capture value from customers, cut costs, redesign, outsource, a source inside
- Off-chain strategy: decommissioning and splitting, selling, and licensing (franchising and buying franchises), acquiring several business units.
6. New product development marketing strategy
A new product is a vital part of an enterprise’s growth and competitive strategy. No manufacturer can survive without developing new products. It can be said that new products are a factor in distinguishing the level of efficiency or success among businesses.
What is considered a new product?
- A completely new product (new function), such as a television, first appeared allowing the transmission of audiovisual symbols.
- New products improve and change the operation of existing functions. For wristwatches, for example, replace the flywheel with a winding pin.
- A new product is a new application of an existing product. For example, aerosols were first developed for spraying pesticides that were later applied to paints.
- The product provides additional new functionality. For example, mobile phones have new features added.
- Existing products for new markets. For example, it is possible to offer private labels to other market areas.
- By reducing costs, the product has new buyers. For example, developing a cheaper laptop.
- Develop a quality upgrade product as a combination of existing products.
- Product development of lower quality level. For example, a manufacturer, instead of buying components, has switched to producing cheaper components on its own and consuming them.
- Product redesigned. For example, the annual change of clothing fashion
New product development and planning process
Step 1: Generate new product ideas
Step 2: Check and evaluate ideas
Step 3: Project plan
Step 4: Product development
Step 5: Test the market
Step 6: Commercialization
7. Product lifecycle Marketing Strategy
All products have a limited shelf life. Each stage of existence in the market has different product consumption, business conditions, level of competition, etc., creating opportunities or challenges for sellers.
Product profitability also varies across life cycle stages. Each stage of the product life cycle requires different marketing, production, financial, and personnel strategies.
The life cycle of a particular product type has distinct characteristics depending on the industry, product, technology and market. From there, the concept of the product life cycle can be introduced, which is a term that describes the dynamics of sales and profits from that product over time.
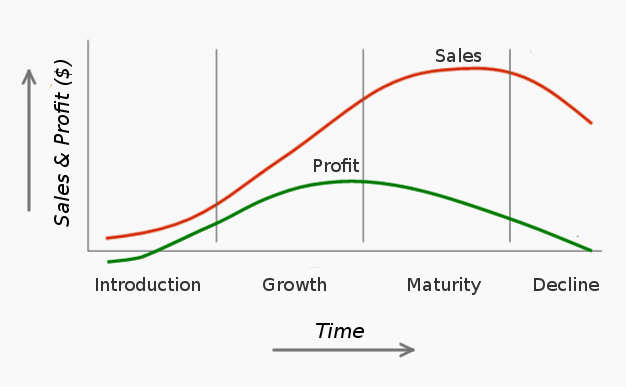
Marketing strategy for the product introduction stage
During the introduction of the product, the production and marketing costs are very high, and because the product is just starting to sell, the sales volume is small, so the profit is very low or no, and competition has not appeared.
The goal of the enterprise in this stage is to make the market accept the product in the shortest time and at the lowest cost. From there, it is necessary to select favorable target market segments to penetrate, but not all market segments.
The main marketing measures that can be used: are a strong advertising campaign to introduce the product; the promotion by-product trial; the use of selective distribution channels, especially direct sales force; and Depending on product and market characteristics, penetration pricing or skimming pricing.
Strategy: Rapid skimming strategy, Gradual skimming strategy, Rapid penetration strategy, and Gradual penetration strategy.
Strategies for the growth phase
At this stage, the market accepts new products, sales volume, and profits market demand increases rapidly, and competitors appear. The goal of that business is to quickly expand market share to occupy a leading position in the market, balancing the two goals of achieving a large market share or high current profits.
To achieve the above goals, businesses need to implement the following strategies and methods of maintaining operations:
- Improve product characteristics and quality or add new models or new features.
- Attack new market segments.
- Develop new distribution channels. Expanding the market by widely distributing selling through many different channels.
- Businesses now switch from advertising to identify products in general to advertising to build images and prestige for their brands.
- The selling price needs to be adjusted to attract customers and limit competitors. If skimming is used initially, it should be gradually reduced to attract lower-income segments.
Marketing strategy in the saturation phase
At this stage, the sales volume does not increase anymore, the level of competition becomes fierce, and the profit of the enterprise that introduces the first product does not keep the desired ratio to the sales volume. The goal of a business is to keep its share of the market and prolong the saturation period to make a profit.
Two types of competitors of existing enterprises are: (1) a few large firms that dominate the market, applying a policy of large sales volume and reducing costs to make a profit, and (2) a large number of competitors appear. Many specialized businesses attack specific market segments and sell specific products.
At this point, businesses can research the market expansion possibilities – and increase sales by:
Sales volume = Number of users x Usage rate, change products or actively change marketing mixture.
Strategies for a Recession
It is the period when sales decreased, goods were stagnant in distribution channels, many businesses in the industry suffered losses, and some small businesses began to withdraw from the market. The cause is due to the appearance of new products or changes in consumer preferences and tastes.
Marketing strategies that businesses can apply during a recession can include:
- Redirecting to exploit the market, and strengthen the competitive position
- Maintain current level of investment while still having loyal customers;
- Selectively reduce business activities, withdraw from market segments that are no longer efficient; and Focus on investing in efficient market segments.
- Harvest to quickly recover capital, avoid damage caused by product stagnation, or reduce the reputation of the business; The important marketing tools in this period are price reduction, promotion, etc.
- Discard the product or dissolve the business unit and move to exploit other opportunities.
8. Conclusion
Businesses need to choose a marketing strategy that is suitable for their market size and goals to maximize revenue and profit. Clearly defining the target customer and market stage is one of the important factors affecting the success of a marketing strategy.
CleverAds, an agency under Clever Group with nearly 15 years of experience, confidently asserts that it is always the ideal destination for businesses to send their products, services, and brand image associated with the goal of the government’s broad recognition wave of customers.




